Fast Realistic Refocusing for Sparse Light Fields
Chao-Tsung Huang1, Jui Chin2,
Hong-Hui Chen2, Yu-Wen Wang1,
Liang-Gee Chen2
1
National Tsing Hua University, Department of Electrical Engineering
2 National Taiwan University, Graduate Institute of
Electronics Engineering
|
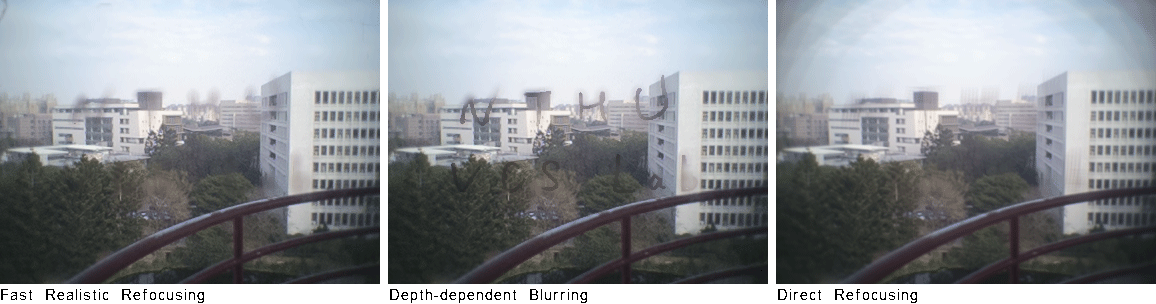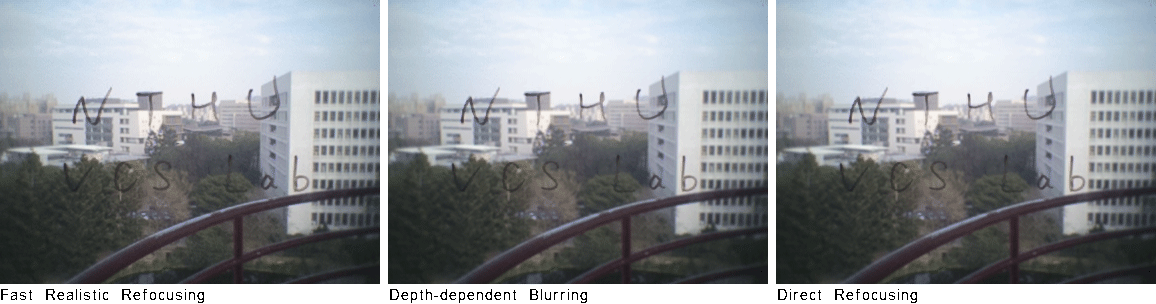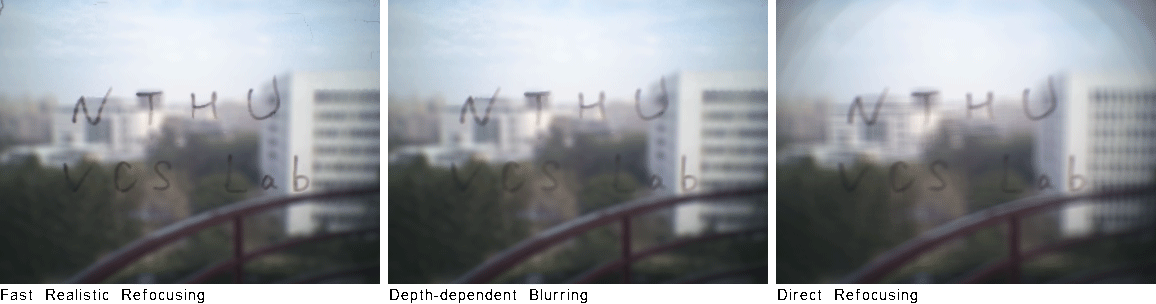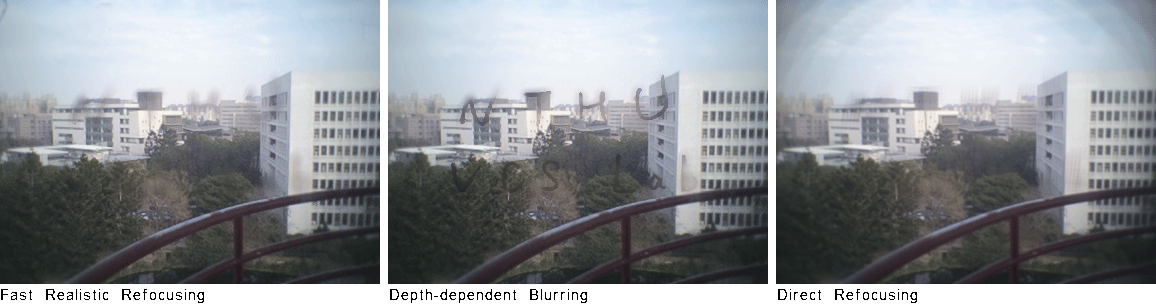
Abstract Digital refocusing for sparsely sampled light fields results in aliasing effect. For realistic quality, previous works performed anti-aliasing by applying time-consuming view interpolation for a heuristic number of novel views. In this paper, we study this problem by first performing a spectral analysis to give an analytical rule for the novel view number, which saves 34% of views compared to the intuitional choice. Then we propose a fast refocusing algorithm using a view interpolation method which is about 30x faster than VSRS-1D-Fast. Experimental results show the effectiveness of our approach in terms of speed and quality. For showing realistic refocusing, a light-field wafer-level-optics array is implemented, and its refocused images are compared to pictures captured by a real camera. Publications "Fast Realistic Refocusing for Sparse Light Fields," Proc. ICASSP, 2015. [preprint, 5.5MB]
|
|
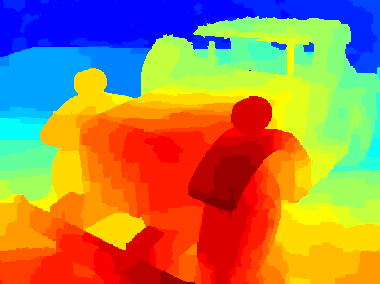
Experimental Refocusing Results Move mouse on the refocused images to activate GIF animation for viewing dynamic refocusing effect (Loading GIFs may take some time) Tsukuba
Truck_d2
Knight_d2
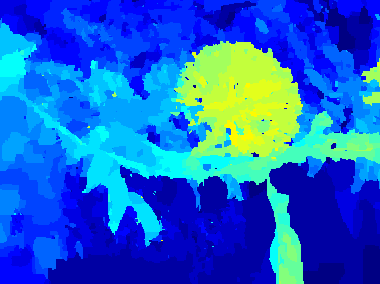
Potato [dataset] (captured by DragonFly)
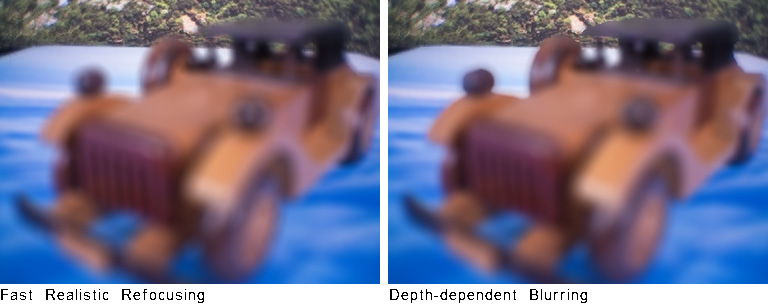
Car [dataset] (captured by DragonFly)
|
|
|
DragonFly: Wafer-level-optics array camera
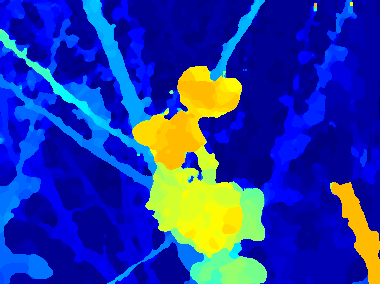
More DragonFly Dataset WordsOnGlass [dataset] (captured by DragonFly)
Grate [dataset] (captured by DragonFly)
Flower [dataset] (captured by DragonFly)
Bicycle [dataset] (captured by DragonFly)
PrunusMume [dataset] (captured by DragonFly) Full aperture (A=2)
Full aperture (A=1)
|
|
Acknowledgement This work was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan, R.O.C. under Grant no. MOST 103-2218-E-007-008-MY3. The authors thank Himax Technologies, Inc., for providing wafer-level optics.
Last update on Feb 12, 2015 |