Difference between revisions of "Research"
(→Millimeter-wave circuits (2012 – present)) |
(→Sponsors) |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
== Terahertz systems (2012 - present) == | == Terahertz systems (2012 - present) == | ||
| − | * NSC project: CMOS THz imaging and detection systems | + | * Funded project |
| + | ** NSC project: CMOS THz imaging and detection systems | ||
== Millimeter-wave circuits (2012 – present)== | == Millimeter-wave circuits (2012 – present)== | ||
| Line 16: | Line 17: | ||
* Transformer-coupled/transmission line coupled amplifiers | * Transformer-coupled/transmission line coupled amplifiers | ||
* Millimeter-wave amplifier linearization techniques | * Millimeter-wave amplifier linearization techniques | ||
| − | * Funded projects | + | * Funded projects |
** NSC project: high linearity reconfigurable W-band transceiver front-end | ** NSC project: high linearity reconfigurable W-band transceiver front-end | ||
** ITRI project: 60 GHz transmitter front-end | ** ITRI project: 60 GHz transmitter front-end | ||
| Line 61: | Line 62: | ||
== Sponsors == | == Sponsors == | ||
* [http://web1.nsc.gov.tw/ National Science Council] | * [http://web1.nsc.gov.tw/ National Science Council] | ||
| + | * [https://www.itri.org.tw/ Industrial Technology Research Institute] | ||
Latest revision as of 10:53, 25 February 2015
My research interests include mm-wave/sub-mm-wave/THz devices, circuits and systems, ultra low power systems, and reconfigurable radio.
Contents
- 1 Featured projects
- 1.1 Ultra low power circuit techniques (2014 - present)
- 1.2 Terahertz systems (2012 - present)
- 1.3 Millimeter-wave circuits (2012 – present)
- 1.4 Diverse heterogeneous integration (2012 – 2014)
- 1.5 Self-healing 4-Gbps reconfigurable CMOS radio-on-a-chip (DARPA Healics program) (2008 – 2012)
- 1.6 Digital controlled artificial dielectric (DiCAD) (2008 – 2009)
- 1.7 High efficiency power amplifier for 3G cellular phone base station (2007 – 2008)
- 1.8 Sponsors
Featured projects
Ultra low power circuit techniques (2014 - present)
(to be updated)
Terahertz systems (2012 - present)
- Funded project
- NSC project: CMOS THz imaging and detection systems
Millimeter-wave circuits (2012 – present)
- 180-GHz high power signal generation
- Multi-band multi-mode millimeter-wave oscillators
- Multi-mode reconfigurable power amplifiers
- Transformer-coupled/transmission line coupled amplifiers
- Millimeter-wave amplifier linearization techniques
- Funded projects
- NSC project: high linearity reconfigurable W-band transceiver front-end
- ITRI project: 60 GHz transmitter front-end
- Industrial collaboration: wireless multimedia and high-speed communication systems
Diverse heterogeneous integration (2012 – 2014)
(to be updated)
Self-healing 4-Gbps reconfigurable CMOS radio-on-a-chip (DARPA Healics program) (2008 – 2012)
|
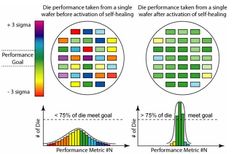
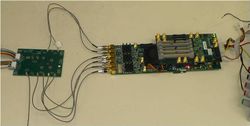
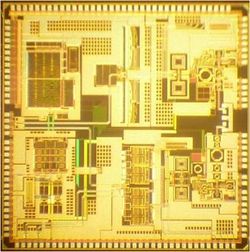
The explosive growth of portable wireless communications has spurred the need for technologies that offer high data rate with low power consumption, low cost, high intergration capability, and small form factor. The 60-GHz spectrum and super-scaled CMOS technology enable these features. However, a major challenge of the advanced technology is the exponential increase in intra-wafer and intra-die process variations that degrade circuit performances.
We proposed a self-healing fully-integrated radio that is compatible with 60-GHz standards and achieves near 100% performance yield with minimum area and power overheads in the presence of extreme technology variations, environmental changes, and long-term ageing. To achieve this goal, this work explores innovative design methodologies in various aspects of design including devices, circuits, and systems. The radio front-end is designed to be extremely tunable allowing for adjustments to be made automatically as the device ages. The self-healing system continually monitors and optimizes its performances throughout the lifetime of the radio. This prototype demonstrates a low overhead highly integrated solution for ultra high speed digital communications.
References: | ||
Digital controlled artificial dielectric (DiCAD) (2008 – 2009)
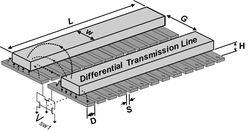
| Artificial dielectric was first used in microwave antenna design in 1948, and reinvestigated by UCLA in 2006 to increase the effective dielectric constant of a transmission line in CMOS technology by inserting floating metal strips underneath a differential transmission line. Switch network was further added to enable digital control of the dielectric constant. Several oscillators, amplifiers, mixers, and phase shifters were implemented based on the DiCAD structure. | |
High efficiency power amplifier for 3G cellular phone base station (2007 – 2008)
(to be updated)